Abstract
Background:
Several phase 2 trials have independently reported high response rates with recombinant interferon treatment in patients with essential thrombocythemia (ET) and polycythemia vera (PV). To further clarify the role of interferon therapy, we carried out a large trial to investigate pegylated-rIFN-α2a (PEG) as therapy in ET/PV patients.
Methods:
MPD-RC 111 (NCT01259817) was an international, multicenter, phase 2 trial evaluating complete and partial response rates (ELN Criteria) toPEG in patients with high-risk ET/PV who were either refractory or intolerant to hydroxyurea (HU) (Modified ELN Criteria). The study was designed to accrue 74 patients with ET and 74 with PV, but it was closed after accrual of 115 patients for administrative reasons. The starting PEG dose was 45 mcg weekly and was titrated for response to a maximum of 180 mcg weekly.
Results
Patients :
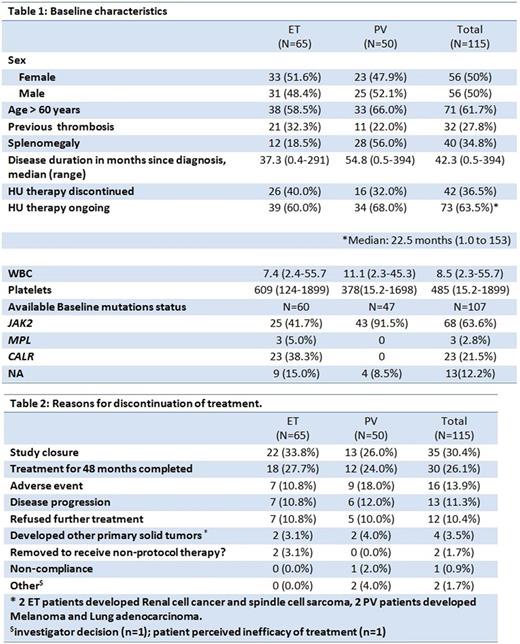
The study enrolled 65 patients with ET and 50 patients with PV from 02/2012 to 12/2015. The median age was 64.0 years (range 20-85) (Table 1). Median time from diagnosis was 37.3 months (0.4-290.9) for ET and 54.8 months (0.5-393.7) for PV, entire cohort 42.3 months (0.5-394). Prior thrombosis was present in 32.3% of ET and 22% of PV patients. Palpable splenomegaly was present in 18.5% of ET patients and 56% of PV patients.
Response
CR / PR (ORR=CR+PR) at 12 months were observed in 43.1% / 26.2% (69.2%) in ET, and 22% / 38% (60%) in PV. The intention-to-treat (ITT) best ORR was 70.8% for ET and 64% for PV. In 77 patients (42 ET and 35 PV) who completed 24 months on-study, the ITT ORR (CR) was 73.8% (47.6%) for ET and 74.3% (42.9%) for PV. Patients with disease duration < 42.3 months had a 71.4% ORR as compared to patients with disease duration > 42.3 months with 57% ORR (p=0.115). Higher treatment doses of PEG were not associated with increase in response rate (mean 118.2 vs 106.2 mcg, p: 0.225). Age <50 years was also not predictive of response (55.6% vs. 68%; p=0.23). For patients with baseline splenomegaly (n=40), 6 had splenic volume reduction of ≥ 10% with median decrease of 2.2% (range -80.3% to +16.3). No major bleeding events developed during the study period. 3 patients had major thrombotic events (2 coronary arterial events and one venous thromboembolic event). One patient with ET transformed to AML, baseline BM biopsy favored pre-fibrotic MF by central review. Transformation to MF occurred in 1 PV patient. 68 patients were evaluable for BM response; BM CR (expert review) was observed in 8 patients (11.1%), 7 of whom achieved BM response only after 24 months of therapy. BM CR was associated with hematologic PR/CR in 7 of the 8 patients. Seven patients progressed to grade 2+ fibrosis (scale 0-3) and the remaining patients had stable BM fibrosis. One patient with a normal karyotype at baseline developed simultaneous +8, +9 clonal abnormalities. Three PV patients, 2 of which JAK2 mutated, lost baseline clonal abnormalities (+1q/dup1q and del(20q) on treatment; all 3 achieved CR at 12 months.
Mutational analysis at baseline was available for 107 patients. JAK2V617F, CALR and MPL mutations are listed in table 1. Additional mutations included ASXL1 in 10, and TP53 in 5 patients. CR rate was higher in CALR mutated patients (56.3% vs. 28.6%, p= 0.02). None of 5 patients with TP53 mutation, and only 3/10 of ASXL1 mutated patients achieved CR.
Safety
Seventy-two % of patients remained on therapy for over 12 months with a median (range) duration of 78.5 (1-245) weeks in ET and 82 (4-209) weeks in PV. The mean (SD) weekly dose of PEG was 102.7 (52.3) mcg for ET and 128.7 (46.4) for PV. The causes for discontinuation of therapy are listed in Table 2. Grade 3 AEs regardless of attribution occurred in 38% of patients. Five grade 4 AEs were reported (AML, depression, hyperuricemia, and 2 subjects with neutropenia). Four non-myeloid malignancies developed in study patients. There were 3 off-trial deaths to date: drug abuse, lung adenocarcinoma, and patient decision unknown.
Conclusions
PEG is an effective agent to treat patients with ET/PV, capable of achieving 12 month ORR in 69% and 60% of ET and PV patients, respectively. The presence of CALR at baseline was associated with superior CR rates in ET. Treatment was associated with significant numbers of AEs which can limit tolerability. Thrombotic events and evolution to MF or AML continued to occur during the treatment period. The effects of PEG on the mutational burdens will be available at the time of presentation. QOL data will be presented separately.
Yacoub: Novartis: Speakers Bureau; Sandoz: Consultancy; CTI: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Mascarenhas: Janssen: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Novartis: Other: DSMB member , Research Funding; Incyte: Other: Clinical Trial Steering Committee , Research Funding; CTI Biopharma: Research Funding; Promedior: Research Funding. Berenzon: Incyte Corporation: Research Funding. Ritchie: Incyte: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Other: Research funding to my institution, and travel, Speakers Bureau; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Other: Research funding to my institution; Celgene: Consultancy, Other: Travel, Speakers Bureau; Astellas Pharma: Other: Research funding to my institution; NS Pharma: Other: Research funding to my institution; Pfizer: Consultancy, Other: Research funding to my institution. Rambaldi: Novartis, Amgen, Celgene, Sanofi: Other: Travel, Accomodations, Expenses; Novartis, Roche/Genentech, Amgen, Italfarmaco: Consultancy. Vannucchi: Novartis: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Shire: Speakers Bureau. Hexner: Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Mesa: Promedico: Research Funding; Incyte Corporation: Research Funding; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Consultancy; Celgene Corporation: Research Funding; Ariad: Consultancy; CTI BioPharma Corp.: Research Funding; Galena Biopharma, Inc.: Consultancy; Gilead Sciences, Inc.: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal